What is RisingWave?
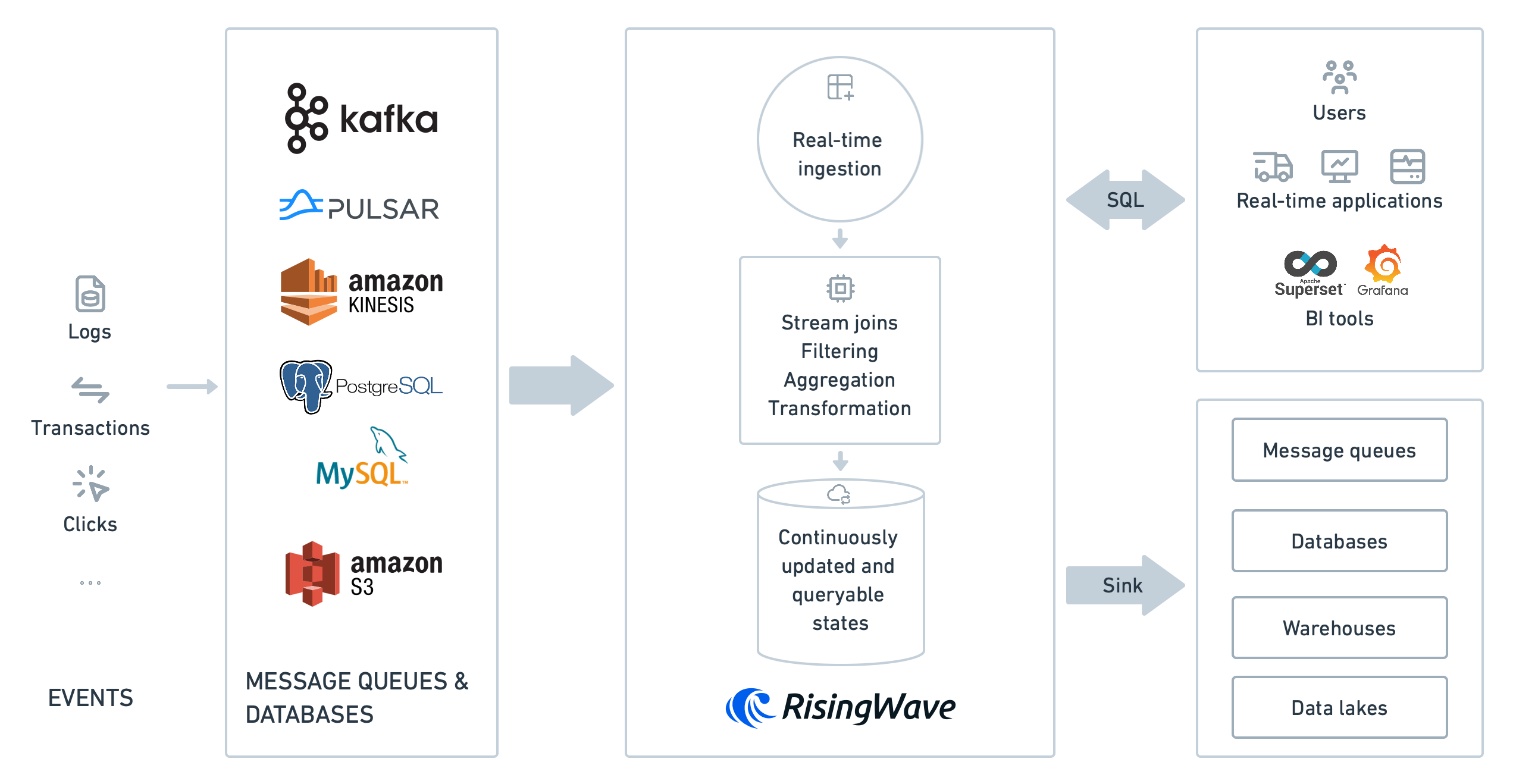
RisingWave accepts data from sources like Apache Kafka, Apache Pulsar, Amazon Kinesis, Redpanda, and materialized CDC sources.
Data in RisingWave can be output to external targets such as message brokers, data warehouses, and data lakes for storage or additional processing.
Is RisingWave a modern alternative to Flink?
Both Apache Flink and RisingWave are stream processing systems. However, RisingWave is more than just a modern alternative to Flink.
If you are looking for a simple, cost-efficient, SQL-based solution for real-time data processing, RisingWave is an excellent choice. RisingWave is designed to be easy to use and can be deployed quickly. This makes it an ideal option for fast-growing businesses that require real-time data processing capabilities.
For a detailed comparison between RisingWave and Flink, see RisingWave vs. Flink.
Use cases
RisingWave can be an excellent fit for these categories of use cases.
They are related categories of use cases. Streaming ETL forms the basis for both real-time analytics and event-driven applications. Real-time analytics expands on streaming ETL by incorporating dashboards, while event-driven applications build on real-time analytics by adding logic to evaluate conditions and trigger follow-up actions.
How does RisingWave work?
SQL as the interface to manage and query data
RisingWave makes it easy to manage streams and data. All you need to interact with RisingWave is Postgres-compatible SQL. No Java or Scala codes are needed.
Real-time results via materialized views
With RisingWave, you define the data you need as materialized views. As new data comes in, RisingWave only performs incremental aggregations as the results for previous events have already been calculated, thus reducing the processing time significantly. To further lower the latency, we optimized the storage processing logic for complex computations and high-concurrency scenarios. Queries can be processed and results can be delivered with low latency even in these demanding circumstances.
Results of materialized views are stored in RisingWave. You can issue a query to find out the latest result of a materialized view.
Elastic and cost-effective
As a cloud-native platform, RisingWave is super elastic. You can dynamically adjust the compute and storage resources based on your actual requirements.
RisingWave is cost-effective. You pay for what you use as you scale. As compute is decoupled from storage in RisingWave, they can be scaled separately. In addition, RisingWave stores data in object storage systems (Amazon S3 and S3-compatible systems). The storage cost is down significantly compared with other centralized solutions that store data in expensive data warehouses.
Data is correct and consistent
When data is processed in batches, if a job goes wrong, you can do some troubleshooting and rerun the job. However, it's not practical to rerun a stream processing job, because the stream never ends. In stream processing, it is crucial that data is calculated correctly and events are not missed or calculated twice. Otherwise, the data will not match the data in upstream or downstream systems.
In RisingWave, data correctness is ensured by a checkpoint-based mechanism. Every time a checkpoint is triggered, the internal states of each operator will be flushed to the cloud storage. When a failover occurs, the operator recovers from the latest checkpoint on the cloud storage.




